Linux Chmod Directory Only
Use the xargs command to speed up the operation by passing multiple entries at once:.

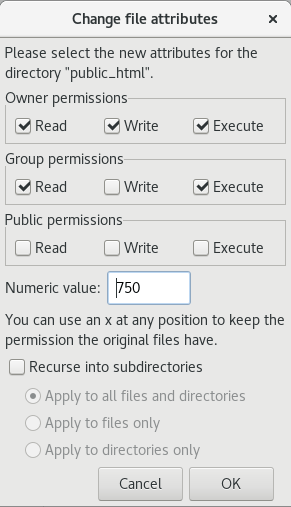
Linux chmod directory only. So, you can use:. Set permission in Linux using chmod:. Second rwx refers to the group permissions.
The X symbolic permission means "execute, if it makes sense" which generally means on directories but not files. For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence:. -type d -exec chmod 770 {} \;.
The format of the command is chmod XXX -R directory-location. In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories). The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command.
Introduction Multi-user systems, such as Linux, require setting up and managing file permissions that ensure only authorized users have access to files they are supposed to. They can’t delete files that belong to someone else, no matter which combination of file permissions are set on the files. In Linux, files and directories are treated similarly.
The basic syntax is:. It is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod:. As you might remember, the default file permission value is 0644, and the default directory’s is 0755.
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. To give execution (search) permission to directories, but not to files, use:. One of the easiest ways is to use the find command to select the files and then run the chmod command with the -exec switch.
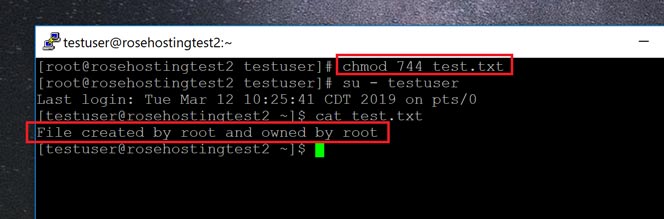
Owner and Groups can Read#. Sudo chown root:root /path/to/application sudo chmod 700 /path/to/application If you look now at permissions with ls -l /path/to/application , you should see the following:. I’ll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod -r.
Each permission may be `on' or `off' for each of three categories of users:. Say you do not want your colleague to see your personal images. Chmod -R +X.
Read (`r'), write (`w'), and execute (`x'). Chmod +s myfile - Set the setuid bit. Type chmod 777 * to change mode for all files in that directory.
There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022. This can be achieved by changing file permissions. If you only want to change mode for a special type of file your can use chmod 777 *.txt *.dat orchmod 777 filename.ext.
It is also used to change special mode flags. Chmod is an abbreviation for change mode;. This entry was posted in Linux and tagged chmod for files only, chmod for folders only, chmod separately for files and directories on July 10, 16 by Sergey Tkachenko.
Linux - Solution 7:. File Permission is given for users,group and others as, SYNTAX :. The lowercase ‘s’ we were looking for is the now a capital ‘S.’This signifies that the setuid IS set, but the user that owns the file does not have execute permissions.
This is a combination of three numbers by which we can represent all. The basic syntax of the chmod command is shown below:. Linux - Newbie This Linux forum is for members that are new to Linux.
Linux File Permissions #. If it is not in the man pages or the how-to's this is the place!. In Linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership.
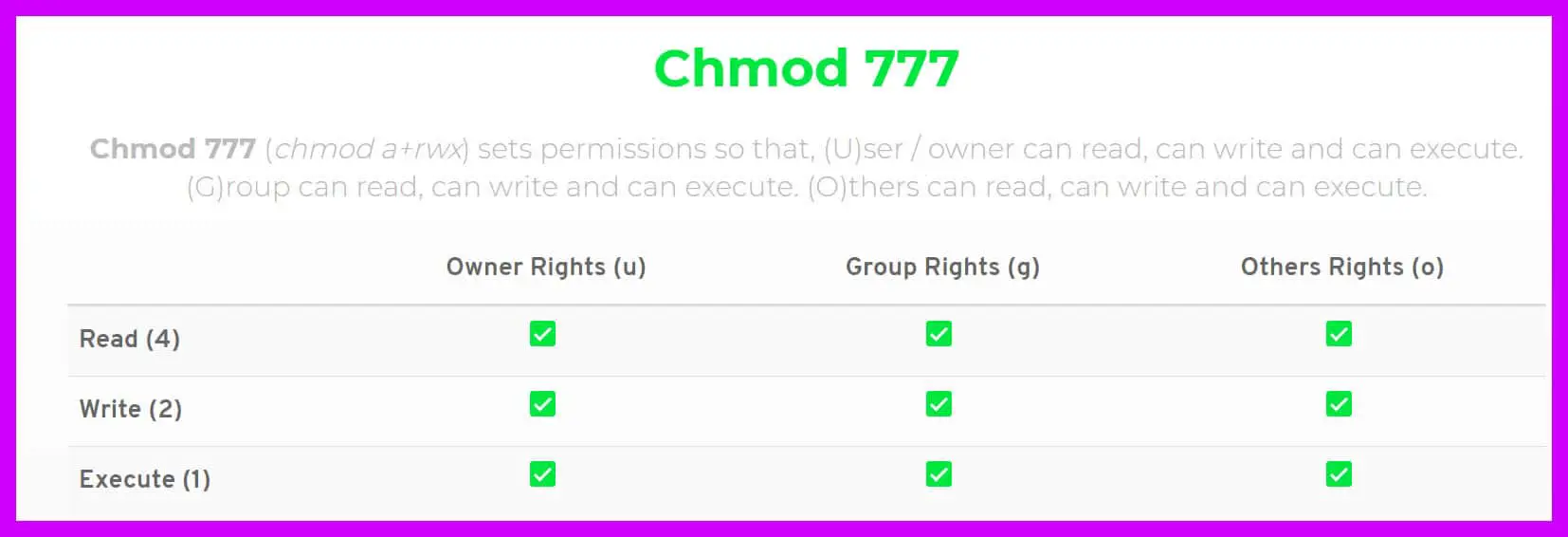
Root@host ~# chmod u+x myfile root@host ~# ls -l total 0 -rwsrw-r-- 1 test test 0 Mar 2. If you ever need to say it out loud, just pronounce it exactly as it looks:. The command executed here is chmod 777 -R home and it gives 777 permission to the folder home itself, also to all of the files and sub-directories inside this folder.
About Sergey Tkachenko Sergey Tkachenko is a software developer from Russia who started Winaero back in 11. This option change files and directories permissions recursively. Examples chmod 644 file.htm.
Is there an easy way out to achieve this on a Linux or Unix-like systems?. Chmod go=rx myfile - Remove read and execute permissions for the group and other. This means the user can only:.
Set the permissions of file.htm to "owner can read and write;. Chmod for changing on Subdirectories# chmod on subdirectories or Files:. Use --no-preserve-root to override this failsafe Linux Permissions Syntax.
Other people in the same group as the owner;. Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone. These permissions apply only on the owner of the file and directory.
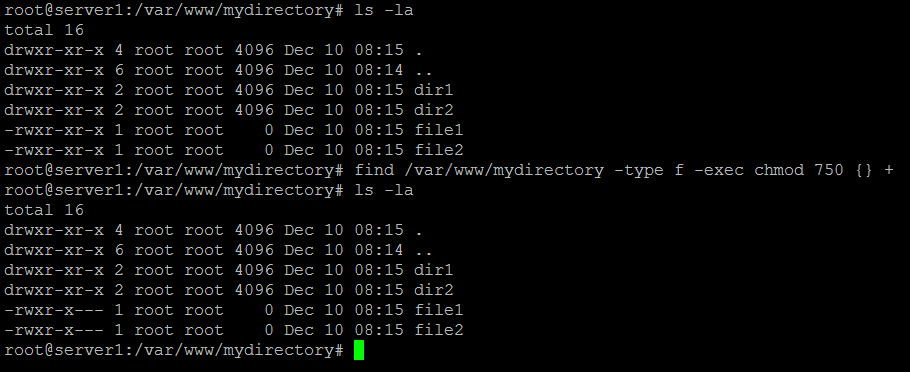
The find command searches for files or directories under /var/www/html and passes each found file or directory to the chmod command to set the permissions. In this UNIX command tutorial we will see how to change file permissions using the chmod command, what are file permissions in UNIX, how to change permissions of directory and sub-directory using UNIX chmod command and finally. Group can read only;.
Apply chmod 755 to directory and sub-directories only (excluding files). Chmod -R rwxrwxrwx path-of-the-directory. Chmod will only have one effect, if you remove all the write attributes of a file then the 'read only' attribute on the Windows file will be set, since this is the same behaviour as CIFS (Common Internet File System) which is the SMB (Server Message Block) client in Linux.
Chmod 755 directory As the user can create a file and delete it, but won't that allow the user to delete other people's files?. It takes the following syntax:. The request is filtered by the umask.
If you want to use an option, you have to place it right after the chmod / chown command. To use chmod, you need to know about access modes.Each file on a Linux system has nine access modes (or settings) that determine exactly who can. How to make a file writeable (chmod 777) Connect to your web server with your telnet software.
Chmod Modifies File Permissions In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions. The Linux command chmod allows you to control exactly who is able to read, edit, or run your files. This Linux option allows you to change permissions or owners of all files and subdirectories inside a specific directory.
Chmod command in UNIX or Linux is used to change file or directory permissions.This is one of many UNIX basic commands which a UNIX or Linux user must be familiar with. How to make a file writeable (chmod 777) Connect to your web server with your telnet software. Chmod file has metadata.
Chmod will change or add metadata depending on. Chmod a=r document.docx 5.2. Write and execute :.
Let's say that I wanted to change the permissions on the current directory and all subdirectories. # alias chmod='chmod --preserve-root' and also add this to your /etc/bashrc or individual user's .bashrc file for permanent changes. Take a look at this example:.
$ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions. The following screenshot shows the execution of the command on a Linux Environment. Just starting out and have a question?.
If you only want to change mode for a special type of file your can use chmod 777 *.txt *.dat orchmod 777 filename.ext. On Linux, the sticky bit only affects a directory—setting it on a file wouldn’t make sense. Chmod 755 $ (find /path/to/base/dir -type d) chmod 644 $ (find /path/to/base/dir -type f).
Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:. When you set the sticky bit on a directory, people can only delete files that belong to them within that directory. There may also a concern about security that permissions specify what a particular user may or may not do changes to a particular file and directory.
Chmod only directories User Name:. -R changes files and directories recursively, while +X sets execute/search only if the file is a directory or already has execute permission for some user. To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all).
The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation. How does chmod work?. Apply chmod 644 to all files only (excluding directory).
This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories. This page explains how to setup read only file permission on Linux or Unix web server such as Nginx, Lighttpd, Apache and more. Using the command, we can set permissions (read, write, execute.
Type chmod 777 * to change mode for all files in that directory. Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions. How can I use, preferably a single chmod command, which will allow any user to create a file in a directory but only the owner of their file (the user who created it) can delete their own file but no one else's in that directory.
The name is an abbreviation of change mode. I have a number of files in this directory and I need to change permission from 0777 to only if that file has 777 permissions. Chmod -R u=rwX,go=rX /path/to/htdocs The only potential problem is that if any of the plain files already have execute set, chmod assumes it's intentional and keeps it.
Chmod command allows you to alter / Change access rights to files and directories. The default umask value is subtracted from the overall file/directory default value. Chmod -R u=rwX,g=rX,o=.
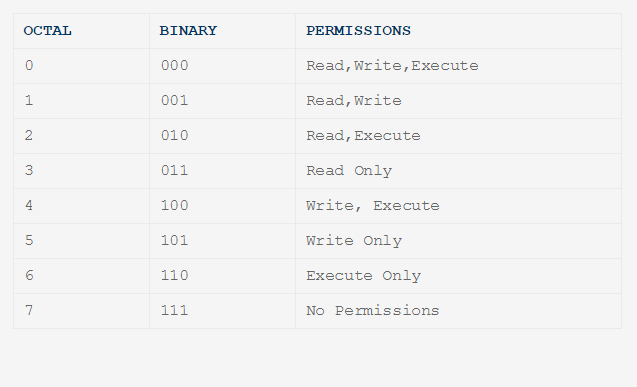
A widely used, often shorter, form of calling chmod is by use of the octal notation. There are three types of permissions that Linux allows for each file. There are three sets of permissions.
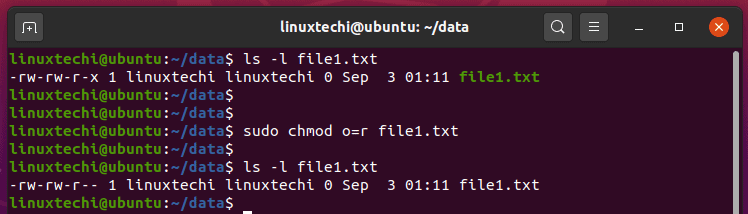
Others can read only". I was thinking to use:. If you need to change a file permission, use the chmod command.
Chown -R 755 /etc/myfiles. Read write execute Putting it all together:. H ow do I set a read-only permission for all of my files stored in /var/www/html/ directory?.
Chmod -R 755 myfiles. Following is a sample of ls -l command output. This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command to change the access permissions of files and directories.
Chmod 1755 participants With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's read-and-write group permissions. When using find with -exec, the chmod command is run for each found entry. Sooner or later in the Linux world, you will have to change the permission on a file or directory.
Chmod options MODE FileName File Permission # File Permission:. PATH chmod read & write read read FileName. -type f -exec chmod 660 {} \;.
Make sure that the owner of the application is root and set the permissions such that only the owner can run it. Using symbols (alphanumerical characters) using the octal notation method. First rwx refers to the user permissions.
How to Set File Permissions Using `chmod' Files and directories in Unix may have three types of permissions:. In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users. Operate on directories only:.
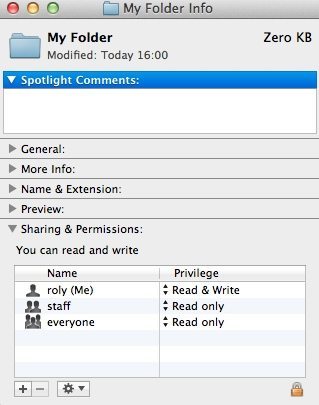
Changing file/directory permissions with 'chmod' command. In Linux, you may face permission problems while installing software packages, exploring directories, reading/writing files. For example, we can make our document read-only for every user and group with:.
User can read, write, and execute;. One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. The man page for chmod doesn't list a way to recursively change permissions on directories only, without affecting the files themselves.
It has -R or –recursive option that change files and directories. Change directory with cd directory. Now if we use chmod, it does not allow to modify root permission # chmod -c --recursive 755 / chmod:.
To assign all the permissions as in your example, use:. How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux. Alot of them are nested, so I can't just chmod the directory and then set the files back to what they were before.
This output looks a little different from what we were expecting. You can use the chmod command to set read-only permission for all files on a Linux / Unix / macOS / Apple OS X / *BSD operating systems. So, in laymen terms, if you wanted a file to be readable by everyone, and writable by only you, you would write the chmod command with the following structure.
Change into the directory with cd, before you run the find command. There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022. Operate on files only:.
Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. Find ./mydir -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;. We can add that permission using the ‘chmod u+x’ command.
To change file access permissions you need to use the chmod command. Chmod directories only I have a lot of directories that I want to chmod, but only the directories, not the files. As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory.
How to chmod files only on Linux There are several ways to apply a chmod to files recursively on Linux. We can use the 'chmod' command which stands for 'change mode'. This is done with the chmod command.
Use chmod to set additional file system modes for files and directories. Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write. Chmod can actually do this itself;.
-rwx------ root root , meaning that root can read, write and. You can set the umask values in /etc/profile or in ~/.bashrc. Change directory with cd directory.
The file or directory owner;. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions. Chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission:.
In this article, I’ll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command.

How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
Linux Chmod Directory Only のギャラリー

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Understanding File Permissions And Access Rights In Linux Linux Stall

Linux Command Line Cheatsheet

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
Chmod Directory Read Write And Type
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

A Quick Reference For Linux Commands One Page Linux Manual Linux Cheating Writing

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

14 04 Chmod Not Working In A Non Super User Ask Ubuntu

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org
Sticky Bit In Linux

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Unix Permissions

9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Write A Unix Linux Find Like Command Myfind In Chegg Com

How To Set Permission For Folders And Subfolders In Linux Poftut

Linux Permissions Deep Dive Part 1 By Runcy Oommen Medium

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Chapter 3 Folder Permissions

Execute Vs Read Bit How Do Directory Permissions In Linux Work Unix Linux Stack Exchange
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsmtof5oge8os R2lzc9s8y8xkmcm3kyhtt M Kqujtci7flb3h Usqp Cau

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
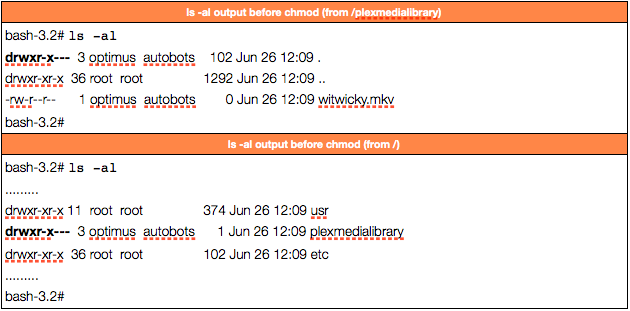
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
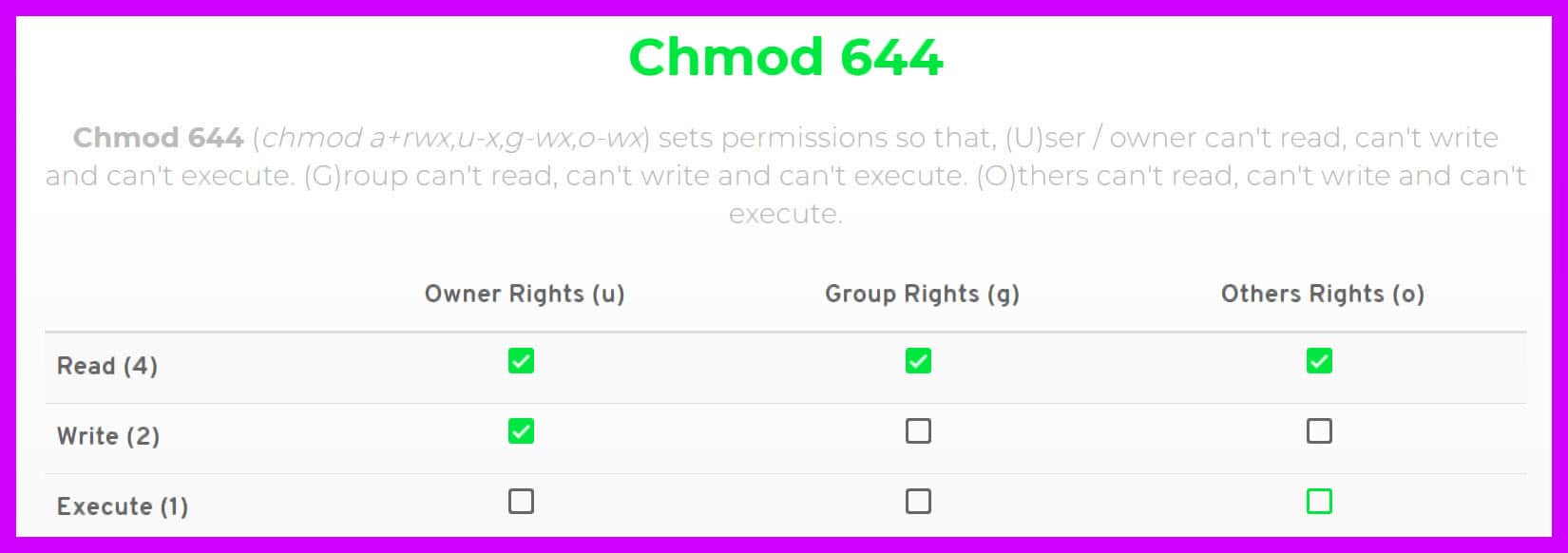
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

File Rights Management In Linux Programmer Sought
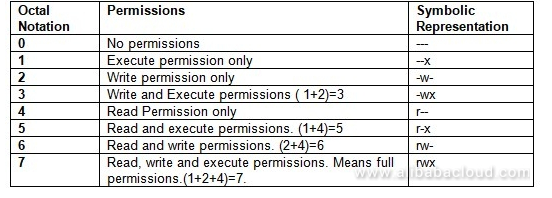
How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
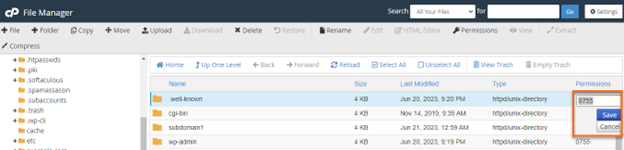
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq2oq90gyu7qjtwwppsiodhgqotjbz3awrstnhczkm6hwgdiahx Usqp Cau

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Change Ownership And Rights To Files And Folders In Linux Smashing Lab

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Advanced File Permissions In Linux
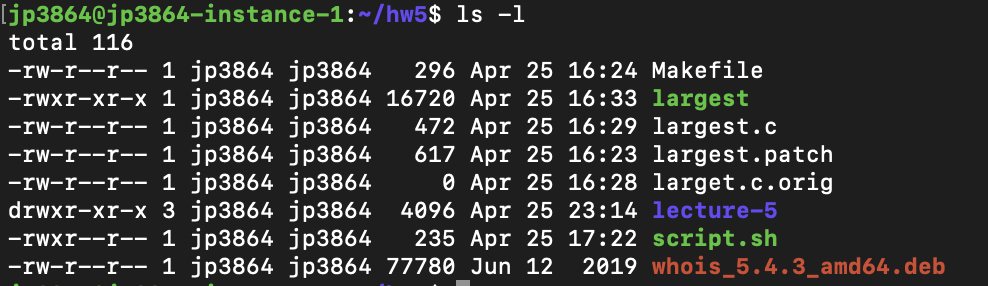
Linux Jessica Peng

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Read Write Access Chmod 775

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Chmod How To Set File And Directory Permission In Linux Using Chmod Youtube
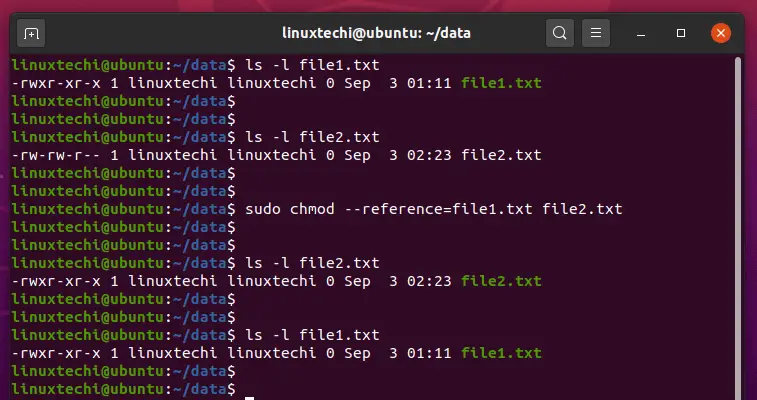
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux
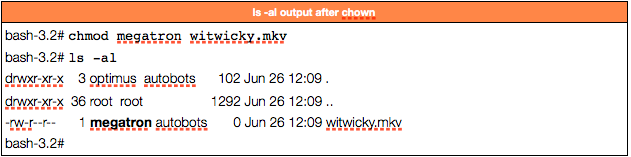
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Command Line I Can T Change Mode For Some Directories Using Chmod Ask Ubuntu

How Do Linux File Permissions Work

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions
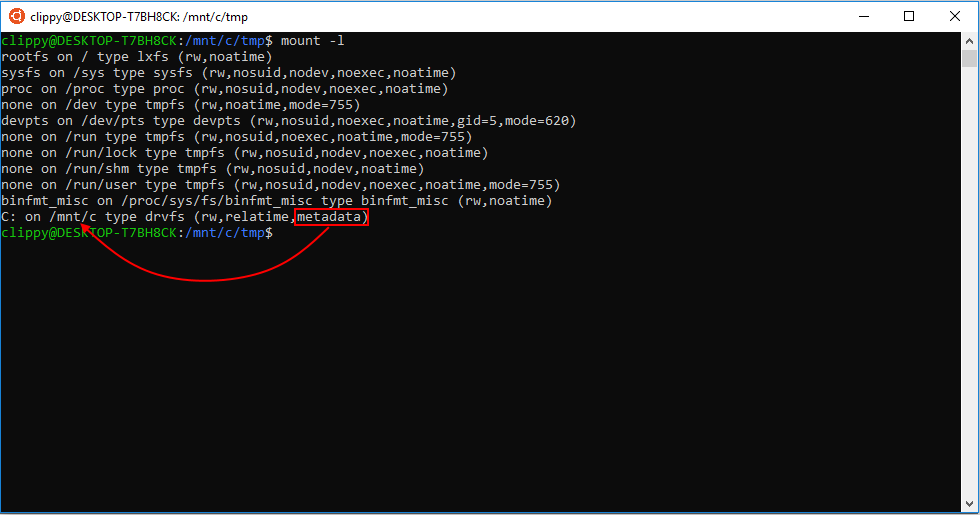
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line
Linux Chmod Tips
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
Change Permissions Of Files And Folders In Filezilla In Your Linux Hosting

Unix Tutorial Five

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
How To Change File Permissions Using The Terminal Chriswrites Com

Change Permission Of Mnt Directory Files Stack Overflow

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc

Directories Showing Up In Green Executable Even After Removing Execute Permission For All Unix Linux Stack Exchange
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Project Ii Six Task Management System Linux File Permissions Programmer Sought
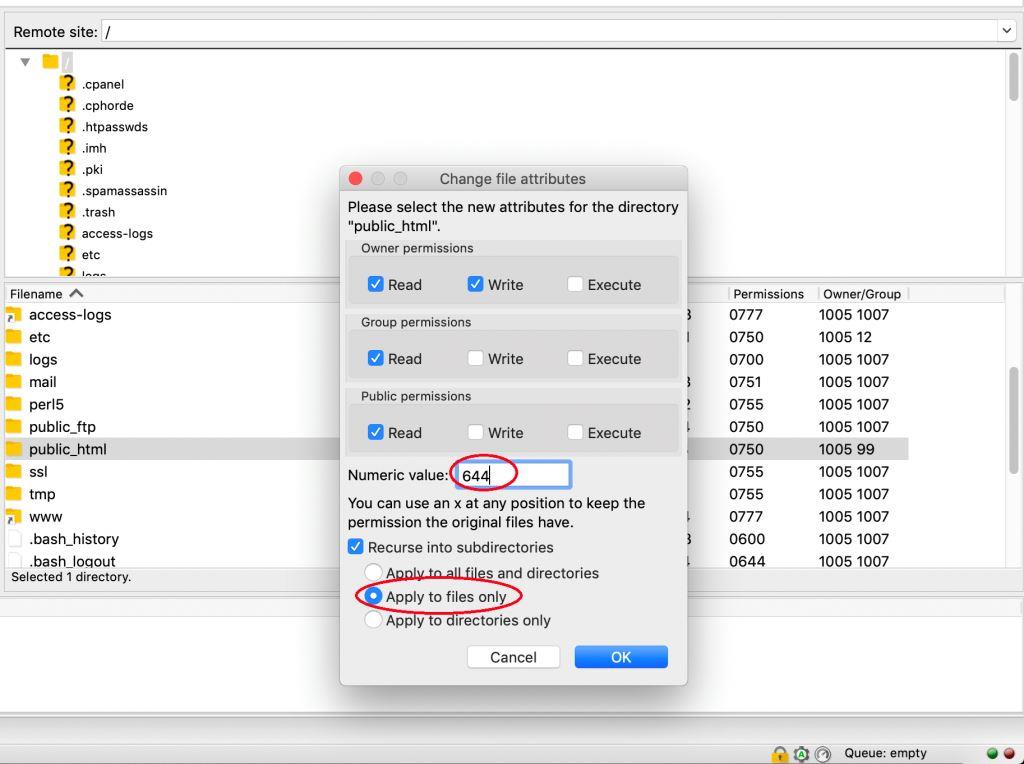
How To Assign The Correct Permissions To My Prestashop Files And Folders Rolige

Linux Chmod To Allow Read And Write Permissions For Directory Super User

File Permissions Rhel 7 Tutorial

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro
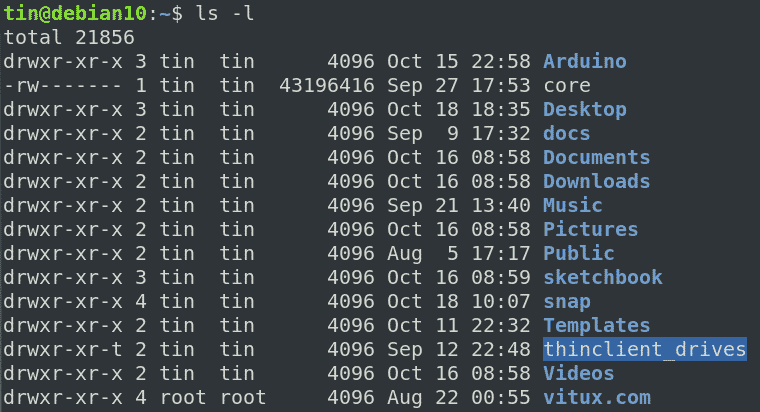
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint
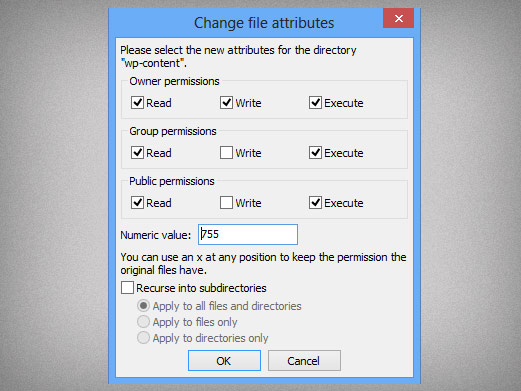
What Is Chmod How To Use Chmod For Wordpress File Permissions

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
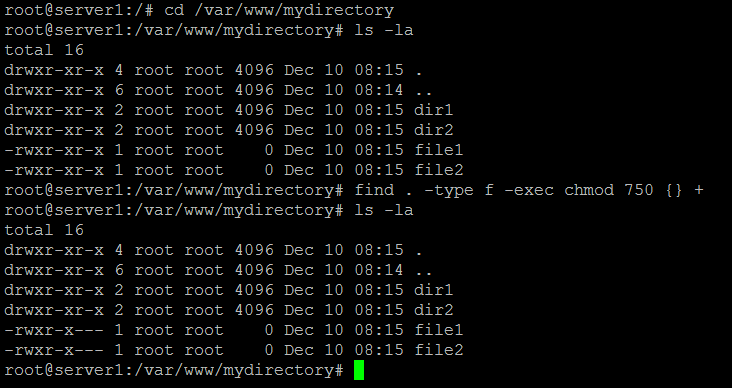
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gct I9jvgnhaxowmpzpaajfkfizchmnvqt Bi Nz3ljrxwqpkb8l Usqp Cau

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Jijo K Jose Jijokjose Personal Website How To Change Permission To A Folder And All Of Its Subfolders In Linux Ubuntu Terminal Jijo K Jose
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport




